Tldr; OEV, also known as Oracle Extractable Value, is a type of MEV created on lending protocols when liquidators close underwater positions. Lending protocols can integrate Oval’s MEV capture mechanism to reclaim OEV.
Key takeaways:
Oracle Extractable Value is a type of MEV created when lending protocols receive oracle updates exposing undercollateralized positions.
MEV searchers close positions to claim a bonus and then use a portion of the bonus to bribe block builders.
Oval, the UMA-developed MEV capture mechanism built with Flashbots’ MEV-Share and Chainlink Data Feeds, uses an order flow auction to redirect OEV back to the protocols that generated it.
MEV and OEV have a major impact on the DeFi ecosystem. MEV is “Maximal Extractable Value”—value that searchers extract by bribing block builders to reorder the contents of a block. Searchers use different strategies to extract value from the ecosystem. One such strategy is liquidating positions on lending protocols to claim OEV, otherwise known as “Oracle Extractable Value.”
While the total sum extracted through MEV strategies is hard to measure, Ethereum’s top lending protocols create hundreds of millions of dollars worth of OEV every year. To date, lending protocols have leaked this value to the MEV supply chain. But with the emergence of MEV capture solutions like Oval, the landscape is changing and lending protocols can earn MEV for the first time. We explain how OEV impacts DeFi and why Oval is a useful mechanism below.
What is OEV?
OEV stands for “Oracle Extractable Value.” OEV is a type of MEV that is created when lending protocols receive an oracle price update that triggers a liquidation.
Liquidators can close positions on lending protocols when the collateral falls below a certain threshold. When an oracle update exposes an underwater position, protocols sell the collateral at a discount. This ensures it gets liquidated swiftly.
MEV searchers repay the debt to claim the collateral for a discount, meaning they receive a bonus. They use part of this bonus to bribe block builders with “tips.” Block builders then pay block proposers to add their blocks to the chain.
In the MEV supply chain, OEV refers to the value block builders and block proposers receive.
How liquidations create OEV
In DeFi, demand for leverage is high. Lending protocols cater to this demand, letting borrowers take out loans when they deposit capital. The borrowers take on a risk here, as they can get liquidated for their collateral.
Lending protocols use oracle updates to establish the value of a borrower’s collateral. When an update exposes an undercollateralized position, MEV searchers can liquidate the position.
Lending protocols aim to liquidate underwater positions swiftly to avoid accruing bad debt. If a borrower defaults and their collateral is worth less than their loan, they are unlikely to repay their debt. In this scenario, lenders suffer as they cannot withdraw their funds.
To incentivize liquidators to close underwater positions, protocols sell the collateral at a discount. This means liquidators (i.e. MEV searchers) receive a bonus, also referred to as a “liquidation penalty,” for repaying the debt. Depending on the protocol and collateral, the bonus typically ranges between 5 and 15%.
The bonus is the maximum theoretical OEV. Searchers compete to make the liquidation and claim the OEV. They must also get their transaction added to a block. To do so, they use a portion of their bonus to bribe block builders, while block builders pay block proposers.
So searchers claim a healthy bonus when they liquidate positions but a portion of this sum goes to other parties in the MEV supply chain. This sum is the OEV.
In short, lending is one of DeFi’s most popular use cases and liquidations are key to DeFi lending. Protocols create OEV during liquidation events.
Capturing OEV with Oval
When lending protocols sell collateral, they sell it at a set discount. They do not capture any value from the OEV created. Oval addresses this issue by finding the true “market price” for the collateral.
Oval is an MEV capture tool that creates a revenue stream for lending protocols. It uses Flashbots’ MEV-Share infrastructure and Chainlink Data Feeds.
MEV-Share changed the DeFi ecosystem by introducing order flow auctions to redistribute MEV to users. Oval builds on this infrastructure to funnel searchers into an auction for the right to liquidate undercollateralized positions.
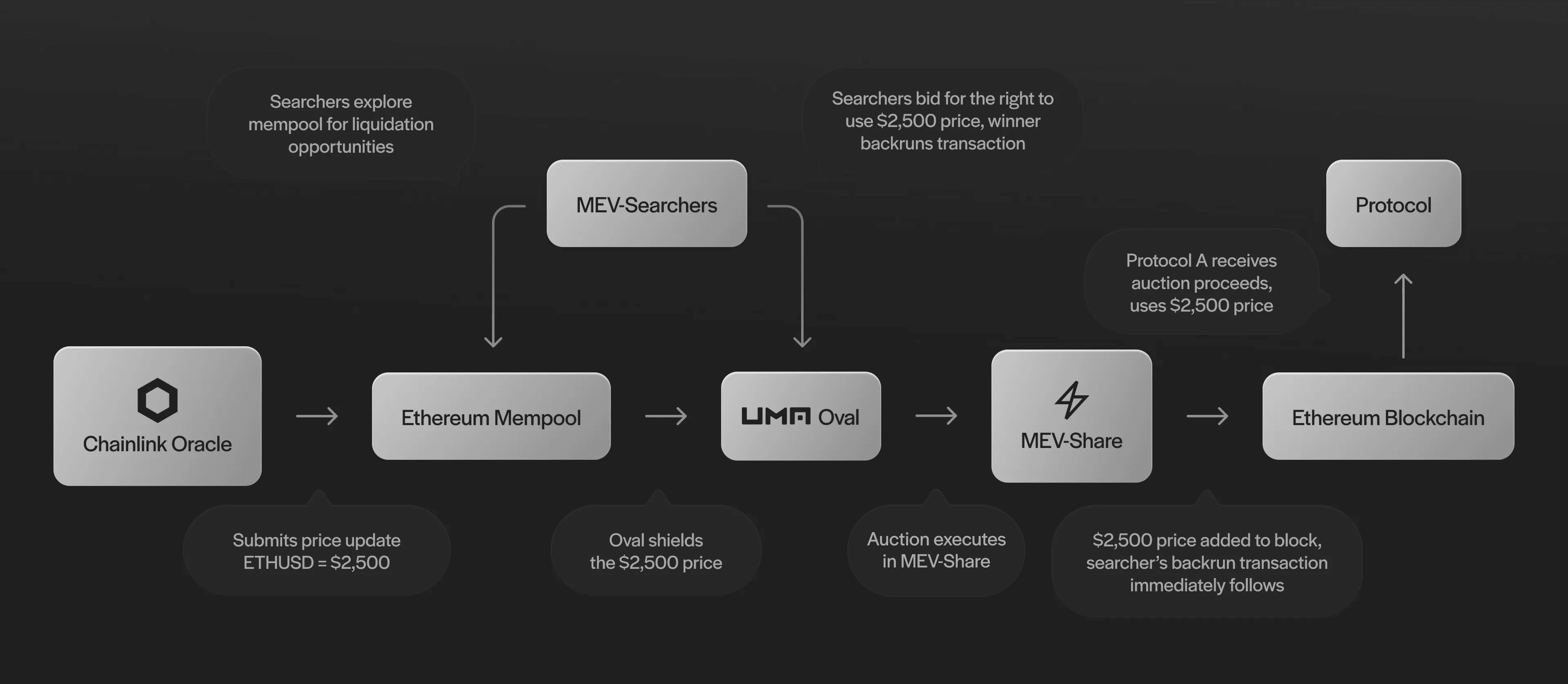
With Oval, searchers bid for the right to use a price served by Chainlink. The auction winner still claims a reward and a portion of their bid goes back to the protocol rather than block builder and proposers.
Searchers don’t lose out on any cash flow. Oval redirects OEV from builders and proposers. But they should still participate because Flashbots sends them so much order flow.
Oval is the first MEV capture mechanism to create a revenue stream for lending protocols. With hundreds of millions of dollars in OEV leaked every year, Oval could prove to be a valuable solution for the ecosystem.
Words by @dreamsofdefi